The Ancient Nashik Timeline is a rich tapestry of mythology, trade, spirituality, and untold struggles. As one of Maharashtra’s holiest and most historic cities, Nashik has stood witness to the rise of empires, the echoes of the Ramayana, flourishing Buddhist teachings, and the silent resilience of local tribes. While modern developments have transformed it into a bustling urban center, Ancient Nashik holds a past that is both powerful and painful.
In this blog, we trace 9 powerful milestones and forgotten struggles that shaped the Ancient Nashik Timeline, uncovering stories hidden in caves, temples, ruins, and scripture.
Read More About Ancient Nashik
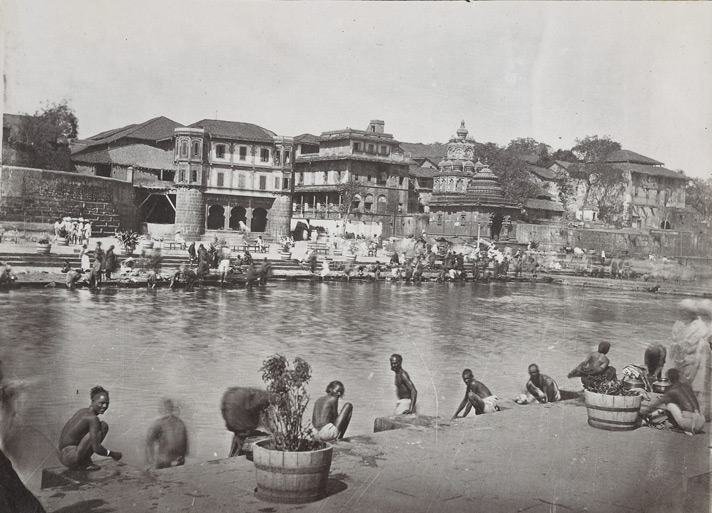
1. Panchavati in the Ramayana: The Mythical Beginning
The Ancient Nashik Timeline arguably begins with Panchavati, a sacred grove that became the epicenter of one of India’s most revered epics the Ramayana. It is believed that Lord Rama, along with Sita and Lakshmana, stayed here during their exile.
- The abduction of Sita by Ravana is said to have occurred on the banks of the Godavari.
- The term Nashik is derived from “Nasika” (nose), referring to the cutting of Surpanakha’s nose by Lakshmana a pivotal moment in the Ramayana.
This mythical origin story imbues the city with spiritual relevance, making it one of the most sacred cities in India and an essential milestone in the Ancient Nashik Timeline.

2. Buddhist Influence & Pandavleni Caves (3rd Century BCE)
In the 3rd century BCE, Nashik witnessed the rise of Buddhism, transforming it into a major religious center. The Pandavleni Caves, a group of 24 rock-cut caves, are significant markers in the Ancient Nashik Timeline.
- Built by Buddhist monks during the Satavahana period, these caves were used as monasteries and meditation spaces.
- Intricate carvings, prayer halls (chaityas), and inscriptions tell stories of devotion and artistic sophistication.
Despite their cultural significance, these ancient caves often remain overshadowed in mainstream tourism — one of the forgotten struggles in preserving Ancient Nashik.

3. Satavahana Dynasty: Prosperity Through Trade (1st Century BCE–2nd Century CE)
One of the most powerful chapters in the Ancient Nashik Timeline is the rule of the Satavahana dynasty, under whom the city became a vibrant trade hub.
- Nashik was strategically located on the trade route connecting Pratishthana (Paithan) to western ports and inland cities.
- Coins and inscriptions found in the region show strong commercial ties with the Roman Empire.
This was a period of economic prosperity and political stability, a truly powerful milestone that transformed Ancient Nashik into a cosmopolitan center.

4. Rise of Jainism and Epigraphic Evidence (2nd–4th Century CE)
While Buddhism thrived, Jainism also left its mark on the Ancient Nashik Timeline. Inscriptions in Brahmi script found near Nashik suggest the presence of Jain monks and shrines.
- Jain traders contributed to Nashik’s economy and cultural development.
- Some caves were later adapted for Jain use, showcasing inter-religious respect and co-existence.
This aspect of Ancient Nashik is often overlooked, yet it played a vital role in shaping its spiritual diversity.

5. Kshatrapa and Abhira Rule: Political Turmoil (4th Century CE)
The 4th century saw a decline in centralized power. The region was ruled by the Western Kshatrapas, followed by the Abhiras.
- Inscriptions suggest conflicts and shifts in governance.
- Art and temple construction slowed during this period.
This was a painful struggle in the Ancient Nashik Timeline, where internal strife impacted both economy and culture.

6. Chalukya & Rashtrakuta Renaissance (6th–10th Century CE)
Under the Chalukyas and later the Rashtrakutas, Nashik witnessed a cultural and architectural renaissance.
- Temples such as the Kapaleshwar Temple were rebuilt or newly commissioned.
- Sanskrit inscriptions from this time highlight royal patronage and local governance structures.
This era revived many powerful traditions and temples, bridging the ancient past with evolving spiritual practices.

7. Seuna (Yadava) Dynasty and Urban Development (12th–14th Century CE)
The Yadava dynasty, which ruled from Devagiri (modern-day Daulatabad), contributed to Nashik’s urban infrastructure.
- Temples, water tanks, and fortifications were strengthened.
- Nashik emerged as a key pilgrimage destination with improved accessibility.
This was a period of positive transformation in the Ancient Nashik Timeline, with city planning and sacred geography taking precedence.

8. Arrival of Islamic Rule and Cultural Syncretism (14th–17th Century)
With the Delhi Sultanate and later Mughal rule, Nashik faced invasions and restructuring.
- Several temples were destroyed or repurposed.
- However, new art forms, languages, and architecture also entered Nashik’s cultural lexicon.
While this era brought struggles, it also created syncretic influences that are visible in local food, language, and heritage — a bittersweet milestone in the Ancient Nashik Timeline.
9. Kumbh Mela Recognition & Colonial Mapping (18th–19th Century)
The Kumbh Mela in Nashik began to gain national attention during the Maratha and early British periods.
- The Trimbakeshwar-Nashik Kumbh was officially documented in colonial records.
- British interest led to the mapping and recording of caves, temples, and forts — albeit often through a Eurocentric lens.
This period helped cement Nashik’s image as a sacred city, even as colonial forces disrupted its autonomy. It marked the formal recognition of its spiritual heritage on a national scale.

Conclusion: A City Carved by Time, Trial, and Triumph
The Ancient Nashik Timeline is not a simple list of dates but a powerful narrative of devotion, struggle, innovation, and transformation. From the echoes of Lord Rama’s exile to the spiritual awakenings in caves, from trade routes linking Rome to temples carved in stone — Nashik is more than just a city; it’s a living timeline.
Yet, many of its milestones remain forgotten, buried under urban sprawl or lost in local memory. Understanding and sharing this history isn’t just about the past — it’s about preserving the identity of a sacred city that shaped Maharashtra, and in many ways, India itself.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the oldest historical site in Nashik?
The Pandavleni Caves, dating back to the 3rd century BCE, are among the oldest sites in the Ancient Nashik Timeline.
Q2. Was Nashik mentioned in the Ramayana?
Yes, Nashik (Panchavati) is where Lord Rama, Sita, and Lakshmana spent part of their exile, and where Ravana abducted Sita.
Q3. Which dynasties ruled over ancient Nashik?
Major rulers include the Satavahanas, Abhiras, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, and Yadavas.
Q4. What religions flourished in ancient Nashik?
Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism all had significant influence during various periods of Nashik's ancient history






Pingback: HAL Tejas Nashik Hub: 7 Breakthroughs & Setbacks in India’s